18 KiB
Detailed Installation Instructions for Various Platforms
Table of Contents
These are beginners guides installation instructions for additional platforms generously provided by users of these platforms. When in doubt, verify the details with the Readme. If you see any issues here while using these instructions, please contribute.
Podman
Podman handles container hostname resolving slightly differently than docker, so you need to make a few changes to the docker-compose.yml to get up and running.
Step 1: Follow the installation instructions from the README, with a few additional changes to the docker-compose.yml.
Edit these additional changes to the docker-compose.yml:
- under
tubearchivist->image:- prefix the container name with
docker.io/(or the url of your repo of choice).
- prefix the container name with
- under
tubearchivist->environment: ES_URL: changearchivist-esto the internal IP of the computer that will be running the containers.REDIS_HOST: changearchivist-redisto the internal IP of the computer that will be running the containers (should be the same as above).- under
archivist-redis->image:- prefix the container name with
docker.io/again.
- prefix the container name with
- under
archivist-redis->expose: - change the whole entry from
expose: ["<PORT>"]into `ports: [":"]. - under
archivist-es->image:- prefix the container name with
docker.io/again.
- prefix the container name with
- under
archivist-es->expose: - change the whole entry from
expose: ["<PORT>"]into `ports: [":"].
Step 2: Create service files (optional)
Since podman doesn't run as a service, it can't start containers after reboots, at least not without some help.
If you want to enable this behavior, you can follow this example to have systemd start up the containers with podman-compose when the computer boots up.
Unraid
Tube Archivist, and all if it's dependencies are located in the community applications store. The three containers you will need are as follows:
- TubeArchivist-RedisJSON: This container acts as a cache and temporary link between the application and the file system. Used to store and display messages and configuration variables.
- TubeArchivist-ES: ElasticSearch stores video meta data and makes everything searchable. Also keeps track of the download queue.
- TubeArchivist: Once your YouTube video collection grows, it becomes hard to search and find a specific video. That's where Tube Archivist comes in: By indexing your video collection with metadata from YouTube, you can organize, search and enjoy your archived YouTube videos without hassle offline through a convenient web interface.
Step 1: Install TubeArchivist-RedisJSON
 This is the easiest container to setup of the thee, just make sure that you do not have any port conflicts, and that your
This is the easiest container to setup of the thee, just make sure that you do not have any port conflicts, and that your /data is mounted to the correct path. The other containers will map to the same directory.
If you need to install TubeArchivist-RedisJSONon a different port, you'll have to follow these steps later on when installing the TubeArchivist container
Step 2: Install TubeArchivist-ES
 ElasticSeach is also pretty easy to setup. Again, make sure you have no port conflicts, make sure that you mapped
ElasticSeach is also pretty easy to setup. Again, make sure you have no port conflicts, make sure that you mapped /usr/share/elasticsearch/data to the same directory as RedisJSON, and make sure to change the default password to something more secure.
There is three additional settings in the "show more settings" area, but leave those as they are.
Step 3: Install TubeArchivist
 It's finally time to set up TubeArchivist!
It's finally time to set up TubeArchivist!
-
Port:Again, make sure that you have no port conflicts on 8000. -
Youtube Media Path:is where you'll download all of your videos to. Make sure that this is an empty directory to not cause confusion when starting the application. If you have existing videos that you'd like to import into Tube Archivist, please checkout the settings wiki. -
Appdata:This should be the same base path as the other two containers. -
TA Username:This will be your username for TubeArchivist. -
TA Password:This will be your password for TubeArchivist. -
RedisThis will be JUST the ip address of your redis container -
ElasticSearch Password:This is the password you defined in theTubeArchivist-EScontainer. -
ElasticSearch:This seems to cause some confusion, but it's a pretty simple step, just replace the IP and Port to match youTubeArchivist-EScontainer.
(example: if your IP is 192.168.1.15, the value should be http://192.168.1.15:9200)
Time Zone:This is an important step for your scheduler, to find your timezone, use a site like TimeZoneConverter
From there, you should be able to start up your containers and you're good to go!
If you're still having trouble, join us on discord and come to the #unraid channel.
Truenas Scale
Truenas Scale can be a bit confusing, with its k3s kubernetes implementation.
However, there is a step by step guide available for it's users here:
https://heavysetup.info/applications/tube-archivist/dataset/
- Ensure you are navigating the columns under
Tube Archiviston the left hand side of the screen
Synology
There are several different methods to install TubeArchivist on Synology platforms. This will focus on the available docker package and docker-compose implementations.
Prepare Directories/Folders
Before we setup TubeArchivist, we need to setup the directories/folders. You are assumed to be logged into the Synology NAS.
1. Docker Base Folder
- Open the
File Stationutility. - Click on the Create🔽 button and choose Create New Shared Folder.
- Name the folder "Docker".
- Add a Description.
- Select the Volume Location.
Note: By default, this will be where all data is stored. Change the folders as best meets your requirements.
- Select the appropriate options from the remaining checkbox configurations.
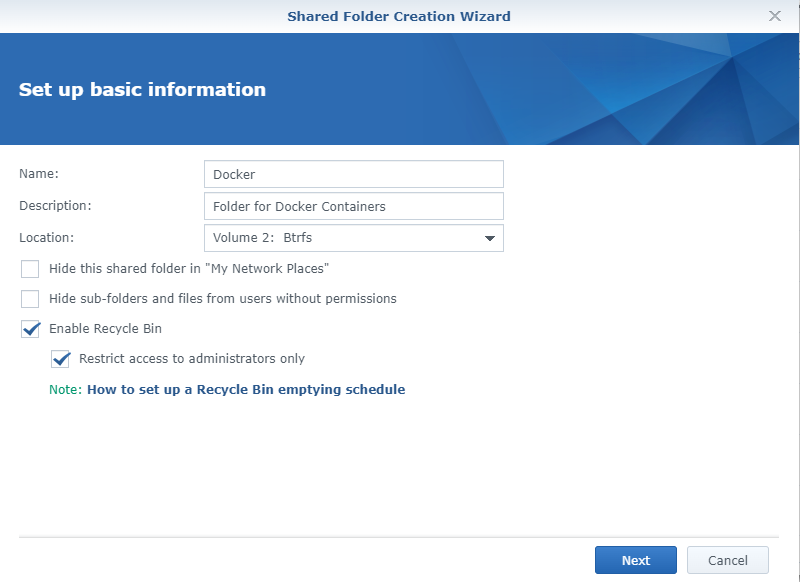
- Click the Next button.
- If you are going to Encrypt your folder, check the appropriate box and provide the Encryption Key and its confirmation.
- Click the Next button.
- On the Advanced Settings page, you can select the Enable data checksum for advanced data integrity setting. This may cause a performance impact, but will allow for potential file self-healing. This cannot be changed later.
Note: This is not recommended, as we will be hosting databases within this folder.
- If you are enabling a quota for how large the folder can get, you can select the Enabled shared folder quota setting and choose the maximum size this folder can grow. This can be changed later.
- Click the Next button.
- Confirm the settings, then click the Apply button. This will create the folder.
2. TubeArchivist Base Folder
- Open the
File Stationutility. - Select the "Docker" folder on the left-hand side.
- Click on the
Create🔽button and choose create Folder. - Name the folder "TubeArchivist".
3. Redis Data
- Open the
File Stationutility. - Select the "Docker" folder on the left-hand side.
- Select the "TubeArchivist" folder beneath "Docker".
- Click on the
Create🔽button and choose create Folder. - Name the folder "redis".
4. Elastic Search Data
- Open the
File Stationutility. - Select the "Docker" folder on the left-hand side.
- Select the "TubeArchivist" folder beneath "Docker".
- Click on the
Create🔽button and choose create Folder. - Name the folder "es".
5. TubeArchivist Cache
- Open the
File Stationutility. - Select the "Docker" folder on the left-hand side.
- Select the "TubeArchivist" folder beneath "Docker".
- Click on the
Create🔽button and choose create Folder. - Name the folder "cache".
6. TubeArchivist Output
- Open the
File Stationutility. - Select the "Docker" folder on the left-hand side.
- Select the "TubeArchivist" folder beneath "Docker".
- Click on the
Create🔽button and choose create Folder. - Name the folder "media".
7. Confirm Folder Structure
Once all of the folders have been created, it should have a folder structure within Docker\TubeArchivist that includes "cache", "es", "media", and "redis" folders.
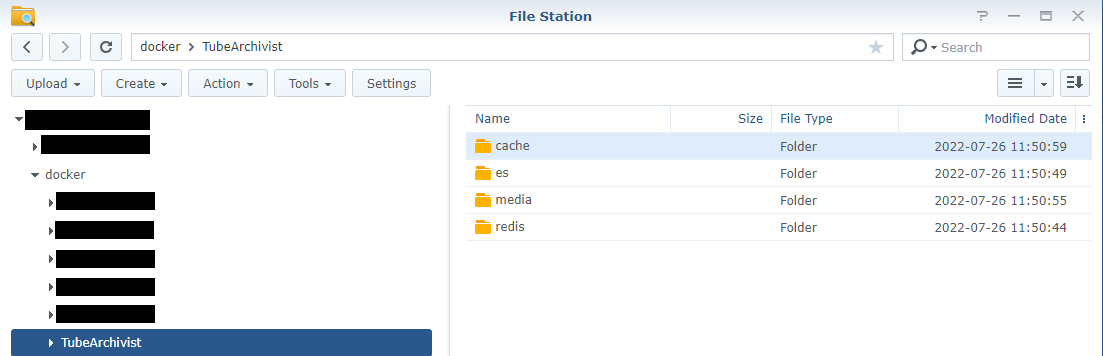
8. Change Permissions - CLI Required
If you do not have SSH access enabled for CLI, enable it before continuing.
- Open the SSH connection to the Synology. Login as your primary
Adminuser, or the user that was enabled for SSH access. - Elevate your access to
root. Steps are provided here. - Change directories to the Volume where the "Docker" folder resides.
Example:cd /volume1 - Change directories to the "Docker" folder.
Example:cd Docker - Change directories to the "TubeArchivist" folder.
Example:cd TubeArchivist - Change the owner of the "redis" folder. If correct, this does not have an output.
Example:chown 999:100 redis - Change the owner of the "es" folder. If correct, this does not have an output.
Example:chown 1000:1000 es - Confirm that the folders have the correct permissions.
Example:ls -hl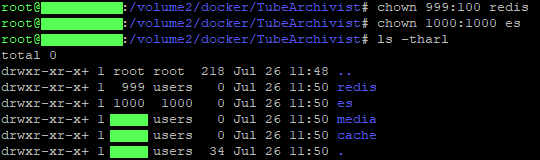
- Logout from root.
Example:logout - Disconnect from the SSH connection.
Example:exit
Docker Setup
- Install the
DockerSynology Package. - Log in to your Synology NAS.
- Open the
Package Centerutility. - Search for
Docker. - Click
Install.
- After
Dockeris installed, open theDockerutility. - Go to the
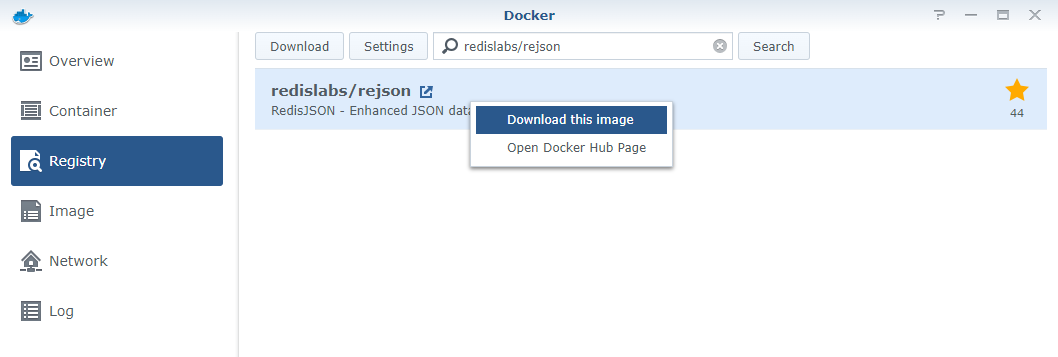
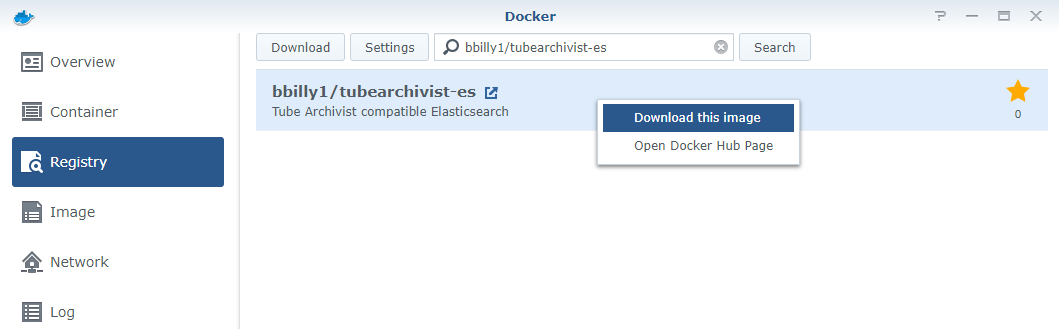
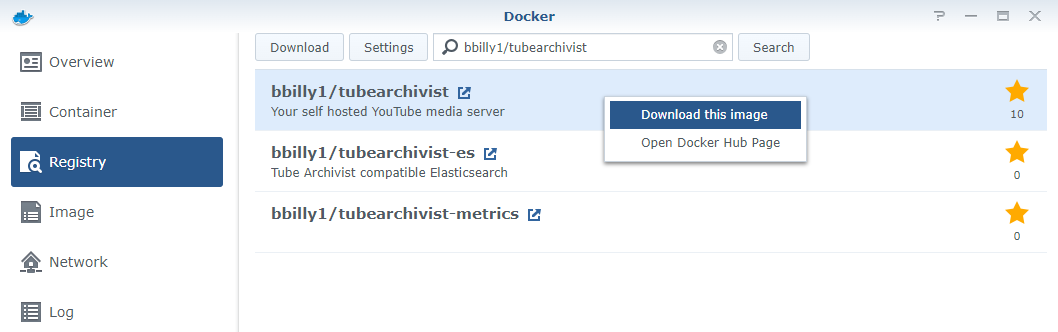
Registrytab. - Search for the following
imagesand download them. Follow the recommended versions for each of the images.
- Go to the
Imagetab. From here, create an container based on each image with the associated configurations below.
-
ElasticSearch
- Select the associated image.
- Click the Launch button in the top.
- Edit the Container Name to be "tubearchivist-es".
- Click on the Advanced Settings button.
- In the Advanced Settings tab, check the box for
Enable auto-restart. - In the Volume tab, click the Add Folder button and select the "Docker/TubeArchivist/es" folder, then type in
/usr/share/elasticsearch/datafor the mount path. - In the Network tab, leave the default
bridgeNetwork (unless you have a specific Network design that you know how to implement). - In the Port Settings tab, replace the "Auto" entry under Local Port with the port that will be used to connect to ElasticSearch (default is 9200).
- In the Port Settings tab, select the entryline for port 9300 and ➖ delete the line. It is not needed for this container.
- The Links tab does not require configuration for this container.
- In the Environment tab, add in the following ElasticSearch specific environment variables that may apply.
- "discovery.type=single-node"
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
- "UID=1000"
- "GID=0"
- "xpack.security.enabled=true"
- "ELASTIC_PASSWORD=verysecret"
- "path.repo=/usr/share/elasticsearch/data/snapshot"
Do not use the default password as it is very insecure. Activating snapshots for backups should only be done after setting the
path.reposetting.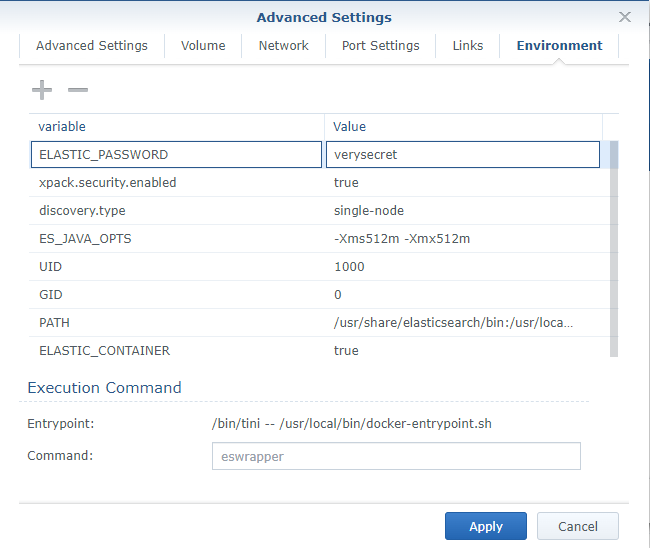
- Click on the Apply button.
- Back on the Create Container screen, click the Next button.
- Review the settings to confirm, then click the Apply button.
-
Redis
- Select the associated image.
- Click the Launch button in the top.
- Edit the Container Name to be "tubearchivist-redis".
- Click on the Advanced Settings button.
- In the Advanced Settings tab, check the box for
Enable auto-restart. - In the Volume tab, click the Add Folder button and select the "Docker/TubeArchivist/redis" folder, then type in
/datafor the mount path. - In the Network tab, leave the default
bridgeNetwork (unless you have a specific Network design that you know how to implement). - In the Port Settings tab, replace the "Auto" entry under Local Port with the port that will be used to connect to Redis (default is 6379).
- In the Links tab, select the "tubearchivist-es" container from the Container Name dropdown and provide it the same alias, "tubearchivist-es".
- In the Environment tab, add in any Redis specific environment variables that may apply (none by default).
- Click on the Apply button.
- Back on the Create Container screen, click the Next button.
- Review the settings to confirm, then click the Apply button.
-
TubeArchivist
- Select the associated image.
- Click the Launch button in the top.
- Edit the Container Name to be "tubearchivist".
- Click on the Advanced Settings button.
- In the Advanced Settings tab, check the box for
Enable auto-restart. - In the Volume tab, click the Add Folder button and select the "Docker/TubeArchivist/cache" folder, then type in
/cachefor the mount path. - In the Volume tab, click the Add Folder button and select the "Docker/TubeArchivist/media" folder, then type in
/youtubefor the mount path. - In the Network tab, leave the default
bridgeNetwork (unless you have a specific Network design that you know how to implement). - In the Port Settings tab, replace the "Auto" entry under Local Port with the port that will be used to connect to TubeArchivist (default is 8000).
- In the Links tab, select the "tubearchivist-es" container from the Container Name dropdown and provide it the same alias, "tubearchivist-es".
- In the Links tab, select the "tubearchivist-redis" container from the Container Name dropdown and provide it the same alias, "tubearchivist-redis".
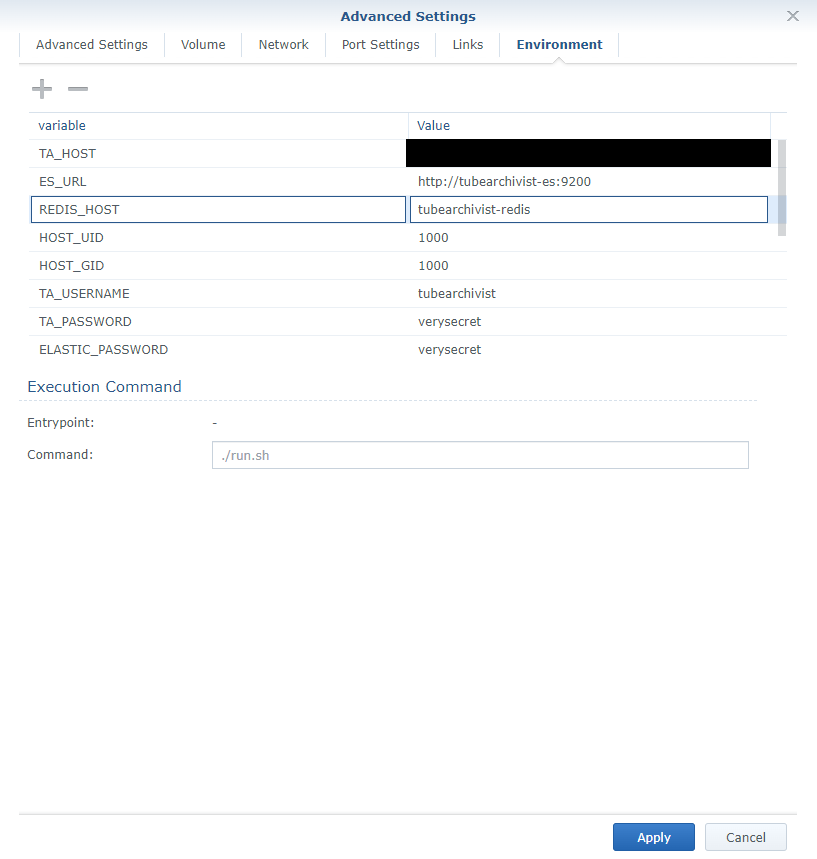
- In the Environment tab, add in the following TubeArchivist specific environment variables that may apply. Change the variables as-is appropriate to your use case. Follow the README section for details on what to set each variable.
- "TA_HOST=synology.local"
- "ES_URL=http://tubearchivist-es:9200"
- "REDIS_HOST=tubearchivist-redis"
- "HOST_UID=1000"
- "HOST_GID=1000"
- "TA_USERNAME=tubearchivist"
- "TA_PASSWORD=verysecret"
- "ELASTIC_PASSWORD=verysecret"
- "TZ=America/New_York"
Do not use the default password as it is very insecure. Ensure that ELASTIC_PASSWORD matches the password used on the tubearchivist-es container.
- Click on the Apply button.
- Back on the Create Container screen, click the Next button.
- Review the settings to confirm, then click the Apply button.
- After the containers have been configured and started, you can go to the Container tab and monitor the containers.
- To review the logs to ensure that the system has started successfully, select the "tubearchivist" container and click on the Details button. In the new window, go to the Log tab. Monitor the logs until either an error occurs or the message
celery@tubearchivist ready.is in the logs. This may take a few minutes, especially for a first time setup.Note: Synology Docker presents the logs in a pagination format. If you are not seeing the logs update, check if there are additional pages.
- After it has started, go to the location in the
TA_HOST. This should give you the standard TubeArchivist login screen.
From there, you should be able to start up your containers and you're good to go!
If you're still having trouble, join us on discord and come to the #synology channel.